- Children from Shijin Kindergarten Made a Study Trip to Shilin UGGp
- Have a spring date with Shilin flowers
- Call for hosts of the 12th International Conference on UNESCO Global Geoparks in 2027
- Call for applications: UNESCO Global Geopark Mentorship Exchange
- Representatives of Changshan Aspring UGGp Visited Shilin UGGp
- Shilin UGGp Visited Xingyi Aspiring UGGp
- Children from Peiqi Kindergarten Visited Shilin UNESCO Global Geopark
Soil, Vegetation, Rare and Threatened Plant Species
Source rocks of soil within the Geopark include:carbonates (limestone dolomitic limestone, dolomite argillaceous limestone), sandstone, shale mudstone, and basalt. Under climate control, soil categories developed from above rocks include 5 types, 8 sub-types, 13 genera, and 48 species. Principal types are red soil, purple soil, and paddy soil.
Biogeographically, the vegetation of the Geopark belongs to the Pan-Arctic plant region, Sino-Himalayan plant subregion, Central Yunan plateau plant zone, a transitional zone between Sino-Himalayan plant province and China-Japan plant province. Subtropical semi-humid evergreen broadleaved forest, sclerophyll evergreen broadleaved forest are indigenous forests.
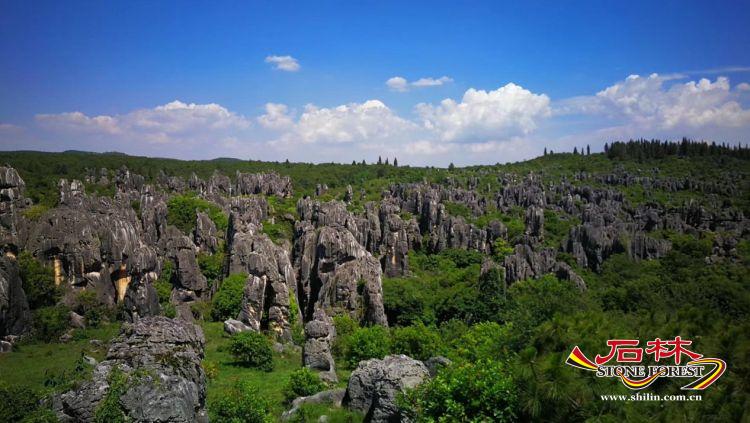

Stone Forest and vegetation (the Major Stone Forest Area)
In the make up of the spermatophyte, tropical types account for 55.4%, and temperate types account for 43.2%. In terms of genera of spermatophyte, representative genera with China-Himalayanelements are Colquhonia, Corallodiscus, Docynia, Lysiontus, Physospermopsis, Prinsepia, Sinocrassula, Siphonostegia, etc. Representative generawith China-Japan elements are Akebia, Conandron, Sinomennium, Platycladus, etc. Representative genera with Eastern Asia elements are Ainsliaea, Bletilla, Codonopsis, Dendrobenthamia, Eriobotrya, Leptodermis, Lycoris, Ophinpogon, Patrinia, Reineckea, etc.
Vegetation type and distribution of Stone Forest Geopark
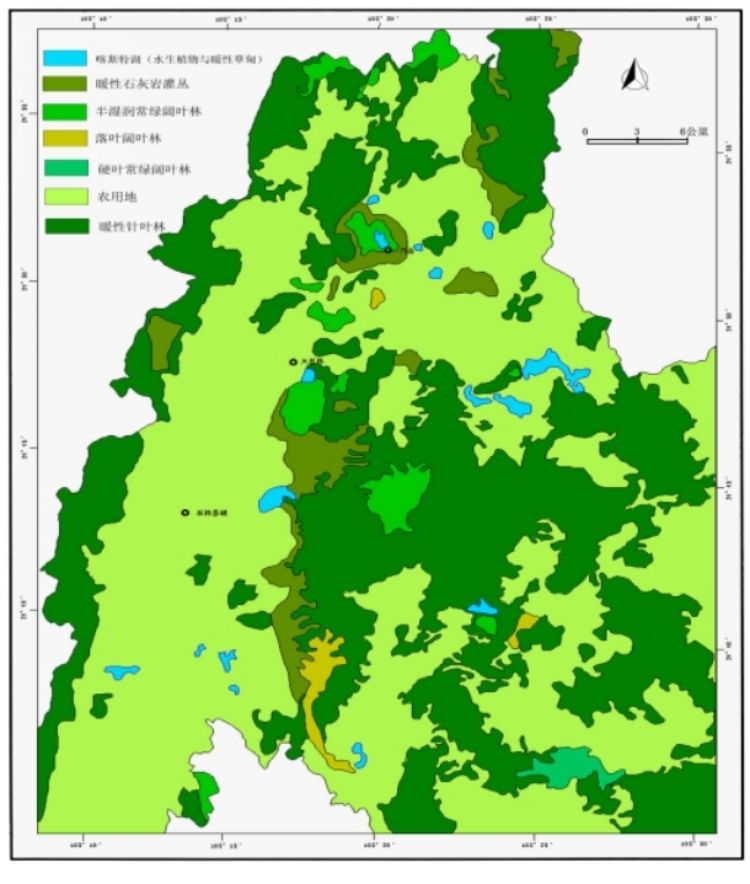
Compared vegetation in eastern China, the vegetation in the Geopark shows some replacement and correspondence features (due to the plateau elevation). Some dominant subtropical evergreen broadleaved species in the east have been replaced by local variants, such as Cyclobalanopsis glauca was replaced by Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides, Castanopsis sclerophylla was replaced by Castanopsis delavayi. Besides, local Cyclobalanopsis delavayi is corresponding to Cyclobalanopsis gilva, local Sapindus delavayi is corresponding to Sapindus mukurosii, local Ehretia corylifolia is corresponding to Ehretia diskisonii, local Albizia mollis is corresponding to Albizia julibrissin, local Pinus yunnanensis is corresponding to Pinus massoniana, local Alnus nepalensis is corresponding to Alnus cremastogyne, local Keteleeria evelyniana is corresponding to Keteleeria, etc.
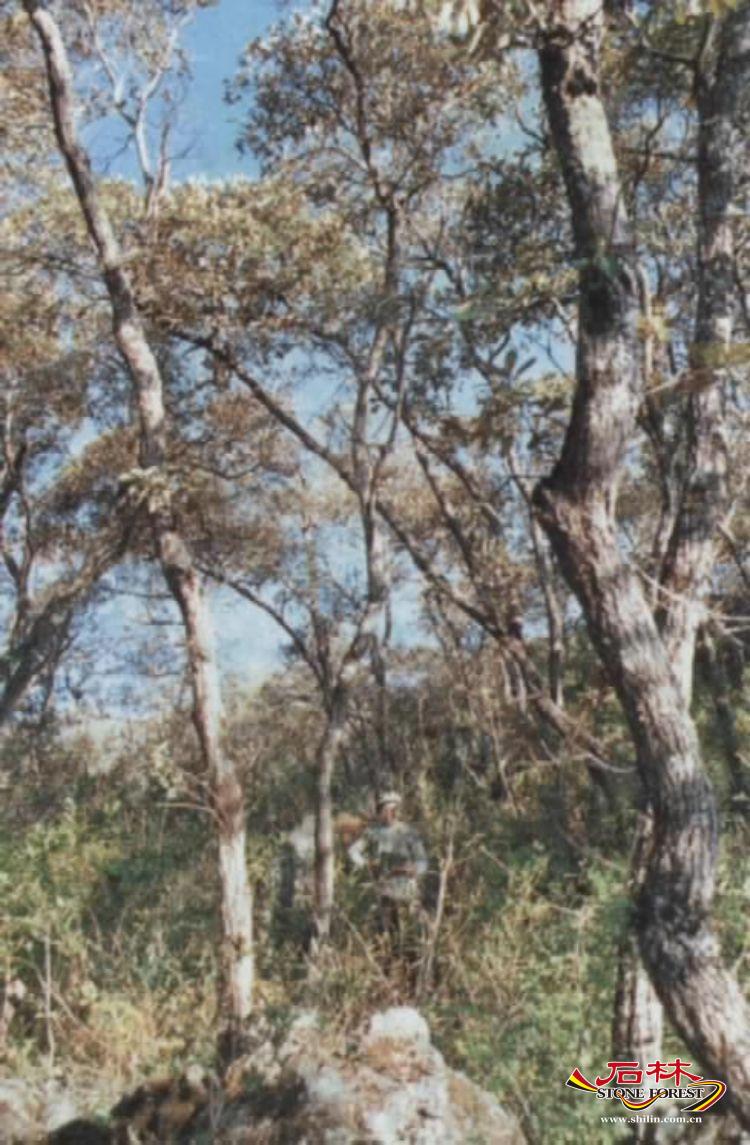

(Quercus cocciferoides )

( Sapindus delavayi)
Certainly, the Geopark also contains some sclerophyll evergreen broadleaved species endemic to southwest China such as Quercus cocciferoides, Quercus franchetii, etc.
The forest coverage is 32 per cent in the park, main forest types are semi-humid evergreen broadleaved forests: Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides forest, Cyclobalanopsis delavayi forest, Castanopsis delavayi forest; sclerophyll evergreen broadleaved forest: Quercus cocciferoides forest, Quercus franchetii forest; warm coniferous forests: Pinus yunnanensis forest, Pinus armandi forest; warm limestone scrub; and coniferous-broadleaved mixed forests. These vegetation types are the typical of vegetation formation of dry-wet monsoon subtropical karst plateau.
Castanopsis delavayi forest is one of the representative evergreen broadleaved forests in slightly dry subtropical area of western China. Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides forest and Cyclobalanopsis delavayi forest are the indigenous slightly dry semi-humid evergreen broadleaved forests of Yunnan-Guizhou karst plateau. Quercus cocciferoides forest and Quercus franchetii forest, which are either relic or direct derivative of the ancient Mediterranean vegetation, are the typical sclerophyll evergreen broadleaved forests endemic to karst mountainous areas of southwest China where the soil is relatively dry. Pinus yunnanensis forest is the typical formation of warm coniferous forests of southwest subtropical areas of China. Cynodon dactylon meadow is the representative karst lake shoal vegetation.
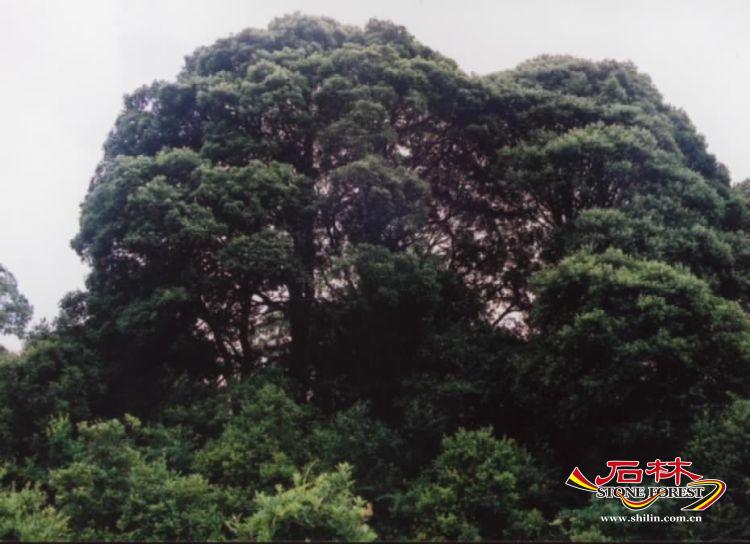

(Castanopsis delavayi)
Within the Geopark, based on incomplete statistics, recorded plants are 97 families, 462 genera, 775 species, of which, fern are 10 families and 21 genera.
Of the 460 spermatophyte species, there are 240 species of semi-humid evergreen broadleaved seed plants, 116 species of sclerophyll evergreen broadleaved seed plants, 192 species of warm coniferous seed plants, 157 species of scrub seed plants, 58 meadow seed plants.
Within the Geopark, there are 8 plant species under national level protection, more than 20 plant species under provincial level protection. Nearly 100 plant species are rare or endemic to Shilin, Kunming or Yunnan.

(Cyclobalanopsis glaucoides)
The rock surface of stone pillars and spires are colonized by plenty of atmogenic algae. Preliminary study shows that they are mostly species of Cyanophyceae and Cyanophyta, 188 alga species, 31 alga genera, 11 families and 4 orders have been identified. Microcystis parasitica, Asterocapsa rubua, Scrytonema bohneri, Scrytonema crustaceum and Asterocapsa atrata, etc. are the dominant species. There are some new species and variants of Chroococcoid and Cyanophyta were found in the Stone Forest, Nephrococcus Shilinensis Tian is the new species found only in Shilin area, it is also the second Nephrococcus species, endemic to China, found by far. New variants include Asterocapsa rubra var. crassa Tian, Asterpcapsa changbaishanensis var. rubra Tian, Asterpcapsa purpurea var. mior Tian.
Observed by naked eye and under microscope, these atmogenic algae take the shape of powder, shell, film, crust, ball, speck, etc. It seems the chemical composition of rock, like Ca0/Mg0 ratio, has much to do with algae type. Rock with low Ca0/Mg0 ratio such as Naigu Stone Forest is usually colonized by Scrytonema bohneri and Microcystis parasitica. Rock with high Ca0/Mg0 ratio such as Major Stone Forest is mainly colonized by Asterocapsa atrata and crytonema crustaceum.
Since organic acid can accelerate solution, algae plays an important role in rock surface micromorphology, particularly surface corrosion of <10 -10'm scale. Algae corrosion features include micro-pit, micro-flute, micro-fissure, micro-hole, micro-spot, etc. Algae demonstrate the bio-karst process.
In addition, algae colonization enriched the color of the stone forest.
The aquatic vegetation of the Geopark, known as Ottelia acuninata flora, is represented by seven typical lake plants: Myriophllum spicatum, Ottelia acuminata var. lunanensis, Hydrilla verticillata, Najas graminea, Potamogeton tepperi, P. malainus, Limnophila sessiliflora. It is the representative lake flora of Yunnan- Guizhou plateau, and Ottelia acuninata is the endemic species.
